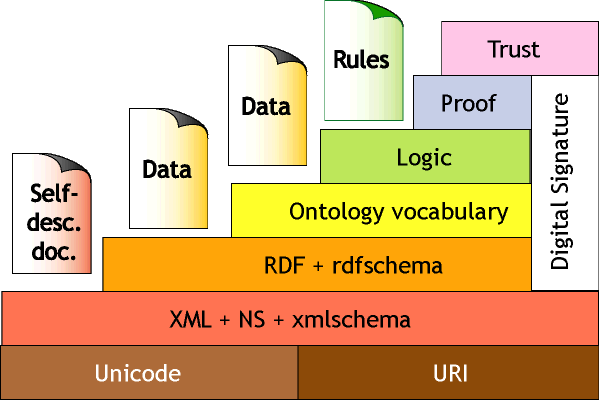
Layered Architecture, sourced from McGuinness (2003) and Berners-Lee (2000)
This improves translatation between the layers to enable human/computer translation. This approach is intended to improve interaction rather than enable computing decision making through artificial intelligence; the emphasis is on decision support for design and manufacture. The detail of this approach and the methodology for automating translation for users is explained in here - http://www.cems.uwe.ac.uk/~phale/#ResearchMethodology. Such techniques as genetic algorithms are outside the scope of this thesis. Instead the emphasis is on clear visualisation, interaction and translation.
This translation code reproduces a taxonomy/ontology and makes it available for modelling/programming systems. This taxonomy/ontology is a copied subset of the main ontology produced as an instance of the main ontology according to model builder choices and for the modelling/programming purposes of that model builder.

Recursive Translation - Automated Copying from ontology to modelling system
Also the translation can link different ontologies/taxonomies together when they are required in order to solve a problem. So the approach is to gather information from ontologies/taxonomies as required for solving a problem as specified by the model builder. This is tested and applied to engineering modelling. An open source approach can be combined with use of open standards ontologies as was advocated by Cheung (2005).
References
Berners-Lee, T., (2000) Semantic Web on XML – Slide 10 [online]. Available from: http://www.w3.org/2000/Talks/1206-xml2k-tbl/slide1-0.html [Accessed 26 June 2008].
Cheung, W. M., Maropoulos, P. G., Gao, J. X., Aziz, H., 2005. Ontological Approach for Organisational Knowledge Re-use in Product Developing Environments. In: 11th International Conference on Concurrent Enterprising - ICE 2005, University BW Munich, Germany.
Eng, N., Salustri, F. A., 2006. "Rugplot" Visualization for Preliminary Design. In: CDEN 2006 3rd CDEN/RCCI International Design Conference University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada.
McGuinness D. L., 2003. Ontologies Come of Age. In: Dieter Fensel, Jim Hendler, Henry Lieberman, and Wolfgang Wahlster, ed. Spinning the Semantic Web: Bringing the World Wide Web to Its Full Potential. MIT Press, 2003 [online]. Available from: http://www-ksl.stanford.edu/people/dlm/papers/ontologies-come-of-age-mit-press-(with-citation).htm [Accessed 26 June 2008].
No comments:
Post a Comment